Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
DPF composite failure workflow#
This example shows how to use the native DPF Python interface to configure and run the composite failure evaluator. It connects the different DPF operators that are needed to evaluate composite failure criteria.
Note
For simple use cases, using the composite failure operator or composite sampling point operator is preferable. For examples, see Composite failure analysis and Sampling point. Additionally, Filter result data by different criteria shows how helper functions can be used to obtain composite result data.
Set up analysis#
Setting up the analysis consists of loading Ansys libraries, configuring the combined failure criterion, connecting to the DPF server, and preparing files.
Load Ansys libraries.
import ansys.dpf.core as dpf
from ansys.dpf.composites.data_sources import get_composites_data_sources
from ansys.dpf.composites.example_helper import get_continuous_fiber_example_files
from ansys.dpf.composites.failure_criteria import (
CombinedFailureCriterion,
CoreFailureCriterion,
CuntzeCriterion,
HashinCriterion,
HoffmanCriterion,
MaxStrainCriterion,
MaxStressCriterion,
TsaiHillCriterion,
TsaiWuCriterion,
VonMisesCriterion,
)
from ansys.dpf.composites.server_helpers import connect_to_or_start_server, version_older_than
Configure the combined failure criterion.
combined_fc = CombinedFailureCriterion(
name="My Failure Criteria",
failure_criteria=[
MaxStrainCriterion(),
MaxStressCriterion(),
TsaiHillCriterion(),
TsaiWuCriterion(),
HoffmanCriterion(),
HashinCriterion(),
CuntzeCriterion(),
CoreFailureCriterion(),
VonMisesCriterion(vme=True, vms=False),
],
)
Start a DPF server and prepare files
Initialize DPF model and data sources#
Initialize the DPF model and the data sources.
rst_data_source = composite_data_sources.result_files
material_support_data_source = composite_data_sources.material_support
eng_data_source = composite_data_sources.engineering_data
if version_older_than(server, "7.0"):
# Get datasources of composite definition files for the backend 2023 R2 or before
composite_definitions_source = composite_data_sources.old_composite_sources["shell"]
else:
# Get datasources of composite definition files for the backend 2024 R1 or later
composite_definitions_source = composite_data_sources.composite
model = dpf.Model(rst_data_source)
Set up providers#
Set up the mesh provider.
mesh_provider = model.metadata.mesh_provider
Set up the material support provider. The material support provider takes care of mapping the materials in the RST file to the materials in the composite definitions. The material support contains all materials from the RST file.
material_support_provider = dpf.Operator("support_provider")
material_support_provider.inputs.property("mat")
material_support_provider.inputs.data_sources(material_support_data_source)
material_support_provider.run()
Set up the result information provider, which gets the unit system from the RST file.
result_info_provider = dpf.Operator("ResultInfoProvider")
result_info_provider.inputs.data_sources(rst_data_source)
Set up the material provider The material provider combines the material support in the engineering data XML file and the unit system. Its output can be used to evaluate material properties.
material_provider = dpf.Operator("eng_data::ans_mat_material_provider")
material_provider.inputs.data_sources = eng_data_source
material_provider.inputs.unit_system_or_result_info(result_info_provider.outputs.result_info)
material_provider.inputs.abstract_field_support(
material_support_provider.outputs.abstract_field_support
)
material_provider.inputs.Engineering_data_file(eng_data_source)
Set up the lay-up provider, which reads the composite definition file and enriches the mesh with the composite lay-up information.
layup_provider = dpf.Operator("composite::layup_provider_operator")
layup_provider.inputs.mesh(mesh_provider.outputs.mesh)
layup_provider.inputs.data_sources(composite_definitions_source)
layup_provider.inputs.abstract_field_support(
material_support_provider.outputs.abstract_field_support
)
layup_provider.inputs.unit_system(result_info_provider.outputs.result_info)
layup_provider.run()
Set up result operators#
Set up result operators for strains and stresses.
rotate_to_global is False because the postprocessing engine expects the
results to be in the element coordinate system (material coordinate system).
strain_operator = dpf.operators.result.elastic_strain()
strain_operator.inputs.data_sources(rst_data_source)
strain_operator.inputs.bool_rotate_to_global(False)
stress_operator = dpf.operators.result.stress()
stress_operator.inputs.data_sources(rst_data_source)
stress_operator.inputs.bool_rotate_to_global(False)
Set up failure evaluator#
Set up the failure evaluator, which combines the results and evaluates all failure criteria. The output contains the maximum failure criteria for each integration point.
failure_evaluator = dpf.Operator("composite::multiple_failure_criteria_operator")
failure_evaluator.inputs.configuration(combined_fc.to_json())
failure_evaluator.inputs.materials_container(material_provider.outputs)
failure_evaluator.inputs.strains_container(strain_operator.outputs.fields_container)
failure_evaluator.inputs.stresses_container(stress_operator.outputs.fields_container)
failure_evaluator.inputs.mesh(mesh_provider.outputs.mesh)
Compute and plot failure criteria#
Use the output of the multiple failure criteria operator to compute the minimum and maximum failure criteria for each element.
minmax_per_element = dpf.Operator("composite::minmax_per_element_operator")
minmax_per_element.inputs.fields_container(failure_evaluator.outputs.fields_container)
minmax_per_element.inputs.mesh(mesh_provider.outputs.mesh)
minmax_per_element.inputs.material_support(material_support_provider.outputs.abstract_field_support)
output = minmax_per_element.outputs.field_max()
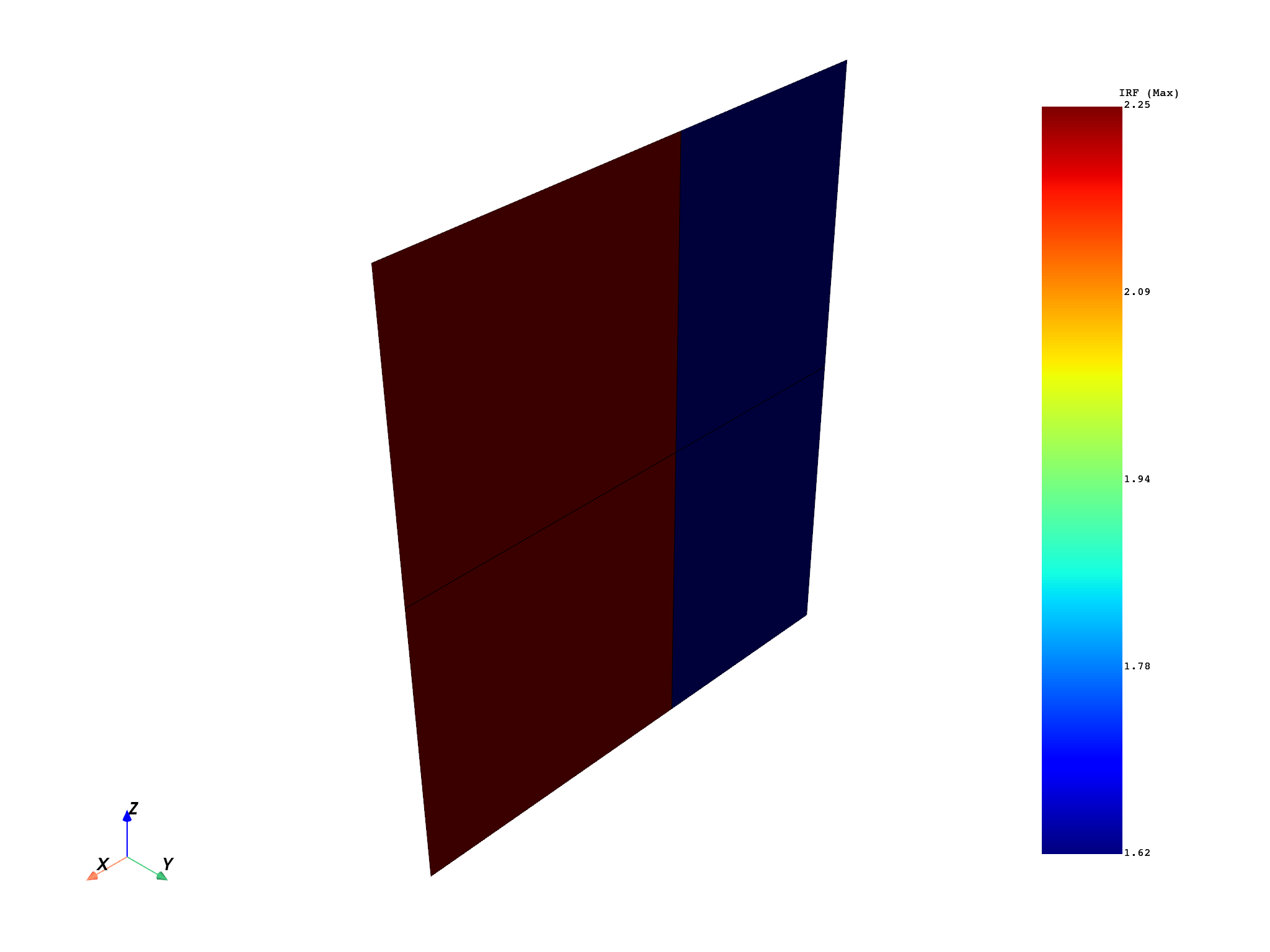
Plot the maximum and minimum values.
value_index = 1
model.metadata.meshed_region.plot(output[value_index])
(None, <pyvista.plotting.plotter.Plotter object at 0x7f59acdc65d0>)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 15.352 seconds)

