Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Postprocess a harmonic analysis#
This example shows how to evaluate failure criteria for a harmonic simulation. It shows how to create a phase sweep to compute the maximum IRF in the frequency-phase space and shows how to identify the critical failure mode and the critical layer.
Note
When using a Workbench project,
use the composite_files_from_workbench_harmonic_analysis()
method to obtain the input files.
Set up analysis#
Setting up the analysis consists of loading the required modules, connecting to the DPF server, and retrieving the example files.
Load Ansys libraries and matplotlib
import ansys.dpf.core as dpf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from ansys.dpf.composites.composite_model import CompositeModel
from ansys.dpf.composites.constants import FAILURE_LABEL, FailureOutput
from ansys.dpf.composites.example_helper import get_continuous_fiber_example_files
from ansys.dpf.composites.failure_criteria import (
CombinedFailureCriterion,
FailureModeEnum,
MaxStressCriterion,
TsaiWuCriterion,
)
from ansys.dpf.composites.layup_info.material_operators import get_material_operators
from ansys.dpf.composites.server_helpers import connect_to_or_start_server
from ansys.dpf.composites.unit_system import get_unit_system
Start a DPF server and copy the example files into the current working directory.
Create a composite model
composite_model = CompositeModel(composite_files_on_server, server)
Define a failure criterion
combined_fc = CombinedFailureCriterion(
name="My Failure Criteria",
failure_criteria=[
MaxStressCriterion(),
TsaiWuCriterion(),
],
)
Obtain stresses and strains and compute max IRF over all phases and frequencies#
Get complex stresses and strains at all frequencies
stress_operator = composite_model.core_model.results.stress.on_all_time_freqs()
stress_operator.inputs.bool_rotate_to_global(False)
strain_operator = composite_model.core_model.results.elastic_strain.on_all_time_freqs()
strain_operator.inputs.bool_rotate_to_global(False)
Get operators that provide material data
material_operators = get_material_operators(
composite_model.data_sources.result_files,
composite_model.data_sources.engineering_data,
get_unit_system(composite_model.data_sources.result_files),
)
Define the frequency sweep. This is relatively coarse so the example does not take too much time.
min_frequency = -180
max_frequency = 180
frequency_step = 60
sweep_phases = range(min_frequency, max_frequency, frequency_step)
Initialize result containers. We create a result container for the failure value, the failure mode and the layer index in which the failure occurs.
# This is a bit confusing, but DPF uses the same label for Frequency and Time
FREQ_LABEL = "time"
PHASE_LABEL = "phase"
all_phases_and_freqs_failure_value_fc = dpf.FieldsContainer()
all_phases_and_freqs_failure_value_fc.labels = [FREQ_LABEL, PHASE_LABEL]
all_phases_and_freqs_critical_layer_fc = dpf.FieldsContainer()
all_phases_and_freqs_critical_layer_fc.labels = [FREQ_LABEL, PHASE_LABEL]
all_phases_and_freqs_failure_mode_fc = dpf.FieldsContainer()
all_phases_and_freqs_failure_mode_fc.labels = [FREQ_LABEL, PHASE_LABEL]
Loop over all the phases and evaluate the failure criterion. The result is added to the field containers declared in the previous cell. In the end each container contains a field for each combination of frequency and phase
for phase in sweep_phases:
# Stress & strains at sweeping phase
stress_at_phase = dpf.operators.math.sweeping_phase_fc(
fields_container=stress_operator, angle=float(phase), unit_name="deg", abs_value=False
)
strain_at_phase = dpf.operators.math.sweeping_phase_fc(
fields_container=strain_operator, angle=float(phase), unit_name="deg", abs_value=False
)
failure_evaluator = dpf.Operator("composite::multiple_failure_criteria_operator")
failure_evaluator.inputs.configuration(combined_fc.to_json())
failure_evaluator.inputs.materials_container(material_operators.material_provider)
failure_evaluator.inputs.stresses_container(stress_at_phase)
failure_evaluator.inputs.strains_container(strain_at_phase)
failure_evaluator.inputs.mesh(composite_model.get_mesh())
# Note: the min/max layer indices are 1-based starting with
# Workbench 2024 R1 (DPF server 7.1)
minmax_per_element = dpf.Operator("composite::minmax_per_element_operator")
minmax_per_element.inputs.fields_container(failure_evaluator)
minmax_per_element.inputs.mesh(composite_model.get_mesh())
minmax_per_element.inputs.material_support(
material_operators.material_support_provider.outputs.abstract_field_support
)
max_for_all_frequencies_at_phase = minmax_per_element.outputs.field_max()
for frequency_id in max_for_all_frequencies_at_phase.get_time_scoping().ids:
output_label = {FREQ_LABEL: frequency_id, PHASE_LABEL: phase}
all_phases_and_freqs_failure_value_fc.add_field(
output_label,
max_for_all_frequencies_at_phase.get_field(
{FAILURE_LABEL: FailureOutput.FAILURE_VALUE.value, FREQ_LABEL: frequency_id}
),
)
all_phases_and_freqs_critical_layer_fc.add_field(
output_label,
max_for_all_frequencies_at_phase.get_field(
{FAILURE_LABEL: FailureOutput.MAX_LAYER_INDEX.value, FREQ_LABEL: frequency_id}
),
)
all_phases_and_freqs_failure_mode_fc.add_field(
output_label,
max_for_all_frequencies_at_phase.get_field(
{FAILURE_LABEL: FailureOutput.FAILURE_MODE.value, FREQ_LABEL: frequency_id}
),
)
Compute maximum over all the phases and frequencies for each element and plot the resulting IRF values
min_max_over_all_op = dpf.operators.min_max.min_max_by_entity()
min_max_over_all_op.inputs.fields_container.connect(all_phases_and_freqs_failure_value_fc)
max_over_freq_and_phases_f = min_max_over_all_op.outputs.field_max()
composite_model.core_model.metadata.meshed_region.plot(max_over_freq_and_phases_f)
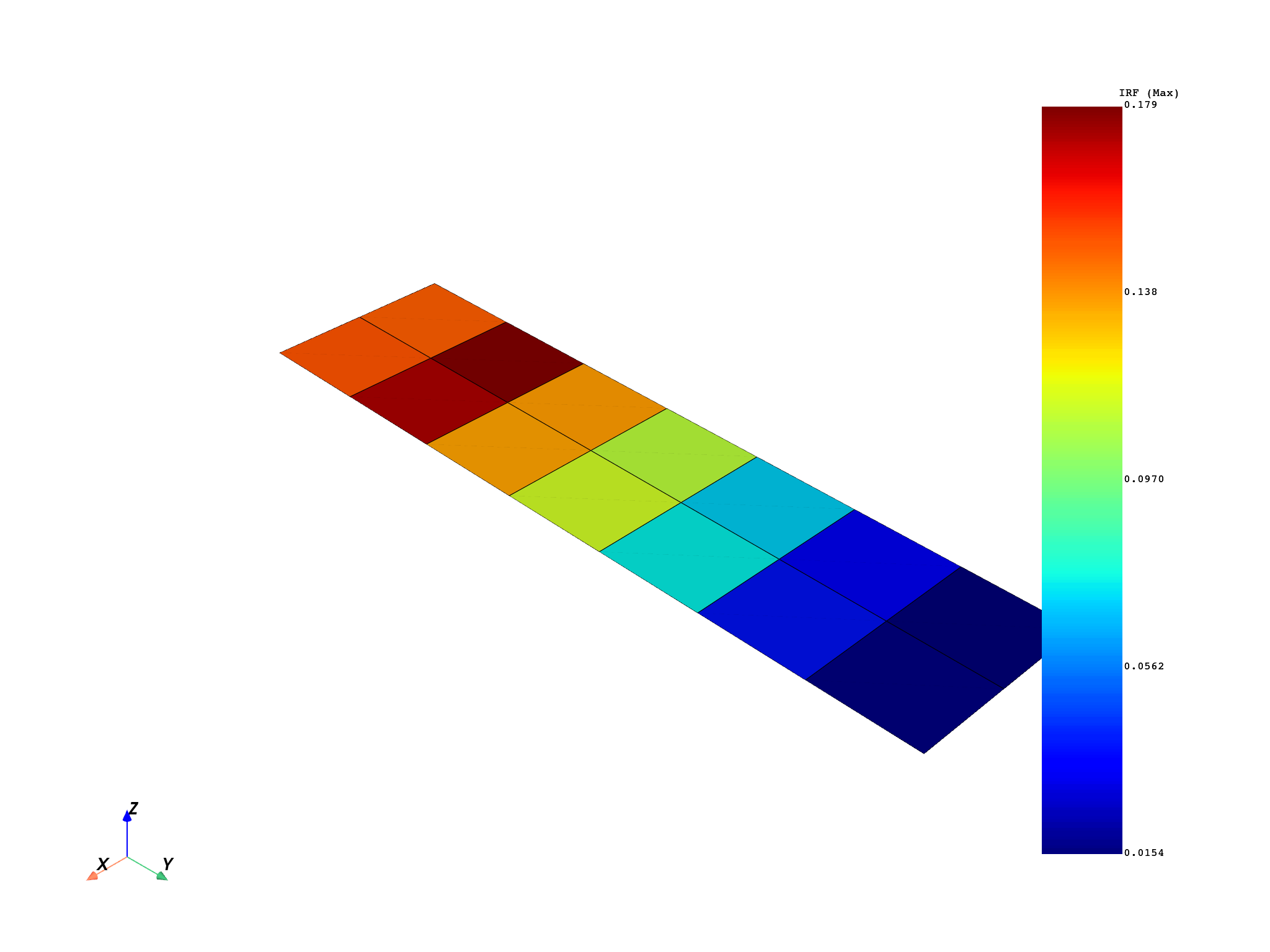
Detailed analysis of the critical element#
Identify the element with the maximum IRF
maximum_element_scoping = max_over_freq_and_phases_f.max().scoping
max_element_id = maximum_element_scoping[0]
print(f"The element with highest IRF is {max_element_id}.")
The element with highest IRF is 3.
Scope container with all frequencies and phases to critical element so we can plot the critical IRF over all the frequencies
rescope_to_crit_element_op = dpf.operators.scoping.rescope_fc()
rescope_to_crit_element_op.inputs.fields_container.connect(all_phases_and_freqs_failure_value_fc)
rescope_to_crit_element_op.inputs.mesh_scoping.connect(maximum_element_scoping)
all_phases_and_freqs_critical_element_fc = rescope_to_crit_element_op.outputs.fields_container()
Compute the maximum IRF over all the phases for each frequency and plot the result for the critical element. Note: this can be different from maximum overall IRF at each frequency, because we look only at the element that has the highest IRF overall.
min_max_over_phases_op = dpf.operators.min_max.min_max_over_label_fc()
min_max_over_phases_op.inputs.fields_container.connect(all_phases_and_freqs_critical_element_fc)
min_max_over_phases_op.inputs.label.connect(FREQ_LABEL)
max_value_for_each_freq_crit_element = min_max_over_phases_op.outputs.field_max()
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1)
frequencies = composite_model.core_model.metadata.time_freq_support.time_frequencies.data
axs.set_xlabel("Frequency (1/s)")
axs.set_ylabel("Max IRF in critical element (-)")
axs.plot(frequencies, max_value_for_each_freq_crit_element.data)
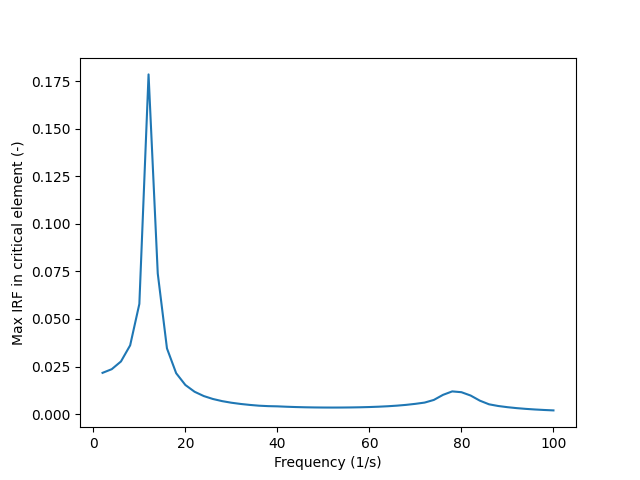
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x7fe22cf339d0>]
Compute the critical phase
freq_id_highest_IRF = max_value_for_each_freq_crit_element.max().scoping[0]
index_highest_IRF = max_value_for_each_freq_crit_element.scoping.index(freq_id_highest_IRF)
critical_phases_over_freqs = min_max_over_phases_op.outputs.domain_ids_max()
critical_phase_at_critical_freq = critical_phases_over_freqs[index_highest_IRF]
print(f"The phase with the highest IRF is {critical_phase_at_critical_freq}°.")
The phase with the highest IRF is -120°.
Compute critical layer and critical failure mode.
max_layer_at_critical_phase_and_time_f = all_phases_and_freqs_critical_layer_fc.get_field(
{FREQ_LABEL: freq_id_highest_IRF, PHASE_LABEL: critical_phase_at_critical_freq}
)
max_layer_index = max_layer_at_critical_phase_and_time_f.get_entity_data_by_id(max_element_id)[0]
all_analyis_plies = composite_model.get_analysis_plies(max_element_id)
critical_ply_name = all_analyis_plies[int(max_layer_index)]
mode_at_critical_phase_and_time_f = all_phases_and_freqs_failure_mode_fc.get_field(
{FREQ_LABEL: freq_id_highest_IRF, PHASE_LABEL: critical_phase_at_critical_freq}
)
critical_mode = mode_at_critical_phase_and_time_f.get_entity_data_by_id(max_element_id)[0]
print(f"The critical ply is {critical_ply_name}.")
print(f"The maximum IRF is {max_over_freq_and_phases_f.max().data[0]}.")
print(f"The critical failure mode is {FailureModeEnum(int(critical_mode)).name}.")
The critical ply is P1L1__ModelingPly.3.
The maximum IRF is 0.17852210868866686.
The critical failure mode is s1c.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 9.879 seconds)

