Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Non-layered structure#
This example demonstrates how to use composite failure operators for non-layered structures with orthotropic materials. It is not preprocessed with ACP. Instead, the example uses a single orthotropic material with defined element orientations and temperature-dependent material properties. The failure criterion operator automatically accounts for temperature dependency when the result file includes temperature data.
You can easily adapt this example to use failure criteria other than Tsai-Wu, such as Hashin or Puck, or to apply a combined criterion. You can also use element and time-step scoping to postprocess only specific elements and load cases.
Setup the environment#
Setup the analysis and initialize the composite model.
import ansys.dpf.core as dpf
from ansys.dpf.composites.composite_model import LayupModelContextType
from ansys.dpf.composites.constants import FailureOutput
from ansys.dpf.composites.data_sources import get_composites_data_sources
from ansys.dpf.composites.example_helper import get_continuous_fiber_example_files
from ansys.dpf.composites.failure_criteria import CombinedFailureCriterion, TsaiWuCriterion
from ansys.dpf.composites.server_helpers import connect_to_or_start_server
Configure the failure criterion#
Define the failure criterion to evaluate. In this example, only Tsai–Wu is selected, but you can combine multiple criteria by using CombinedFailureCriterion.
combined_fc = CombinedFailureCriterion(
name="failure of all materials",
failure_criteria=[
TsaiWuCriterion(dim=3),
],
)
Prepare the data sources (inputs)#
composite_data_sources = get_composites_data_sources(composite_files_on_server)
rst_data_source = composite_data_sources.result_files
material_support_data_source = composite_data_sources.material_support
eng_data_source = composite_data_sources.engineering_data
Load the model and configure the operators#
Use the DPF Composites launch server, which automatically loads all required plugins.
Prepare inputs for the composite operators.
mesh_provider = model.metadata.mesh_provider
result_info_provider = dpf.Operator("ResultInfoProvider")
result_info_provider.inputs.data_sources(rst_data_source)
Load the materials from the XML file. It is important to ensure that the Transfer IDs (VUID) in both the XML and RST files match so the material properties map correctly to the elements.
material_support_provider = dpf.Operator("support_provider")
material_support_provider.inputs.property("mat")
material_support_provider.inputs.data_sources(material_support_data_source)
material_support_provider.run()
material_provider = dpf.Operator("eng_data::ans_mat_material_provider")
material_provider.inputs.data_sources = eng_data_source
material_provider.inputs.unit_system_or_result_info(result_info_provider.outputs.result_info)
material_provider.inputs.abstract_field_support(
material_support_provider.outputs.abstract_field_support
)
material_provider.inputs.Engineering_data_file(eng_data_source)
Select the time step by setting a time scope.
scope_config = dpf.DataTree()
scope_config.add({"requested_times": 1})
scope_config_reader_op = dpf.Operator("composite::scope_config_reader")
scope_config_reader_op.inputs.scope_configuration(scope_config)
The evaluate_failure_criterion_per_scope operator handles all background details. For example, it accounts for temperature‑dependent material properties if the result file includes temperature data.
evaluate_failure_criterion_op = dpf.Operator("composite::evaluate_failure_criterion_per_scope")
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.scope_configuration(scope_config_reader_op.outputs)
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.criterion_configuration(combined_fc.to_json())
# Set the element scope. This example uses the entire meshed region,
# but you can scope specific elements to process only a subset.
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.element_scoping(model.metadata.meshed_region.elements.scoping)
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.materials_container(material_provider.outputs)
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.stream_provider(model.metadata.streams_provider)
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.mesh(mesh_provider.outputs.mesh)
# The operator requires the layup model context to interpret the inputs correctly.
# In this example, no ply information is provided because all elements are homogeneous.
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.layup_model_context_type(LayupModelContextType.NOT_AVAILABLE)
# This workflow does not support sandwich failure criteria.
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.request_sandwich_results(False)
Extract the maximum failure value per element.
minmax_per_element = dpf.Operator("composite::minmax_per_element_operator")
minmax_per_element.inputs.fields_container(evaluate_failure_criterion_op.outputs.failure_container)
minmax_per_element.inputs.mesh(mesh_provider.outputs.mesh)
minmax_per_element.inputs.material_support(material_support_provider.outputs.abstract_field_support)
Plot the results#
Set the scalar bar range to [0, 1]. A failure value of 1 means the criterion is satisfied exactly; values greater than 1 indicate that failure has occurred.
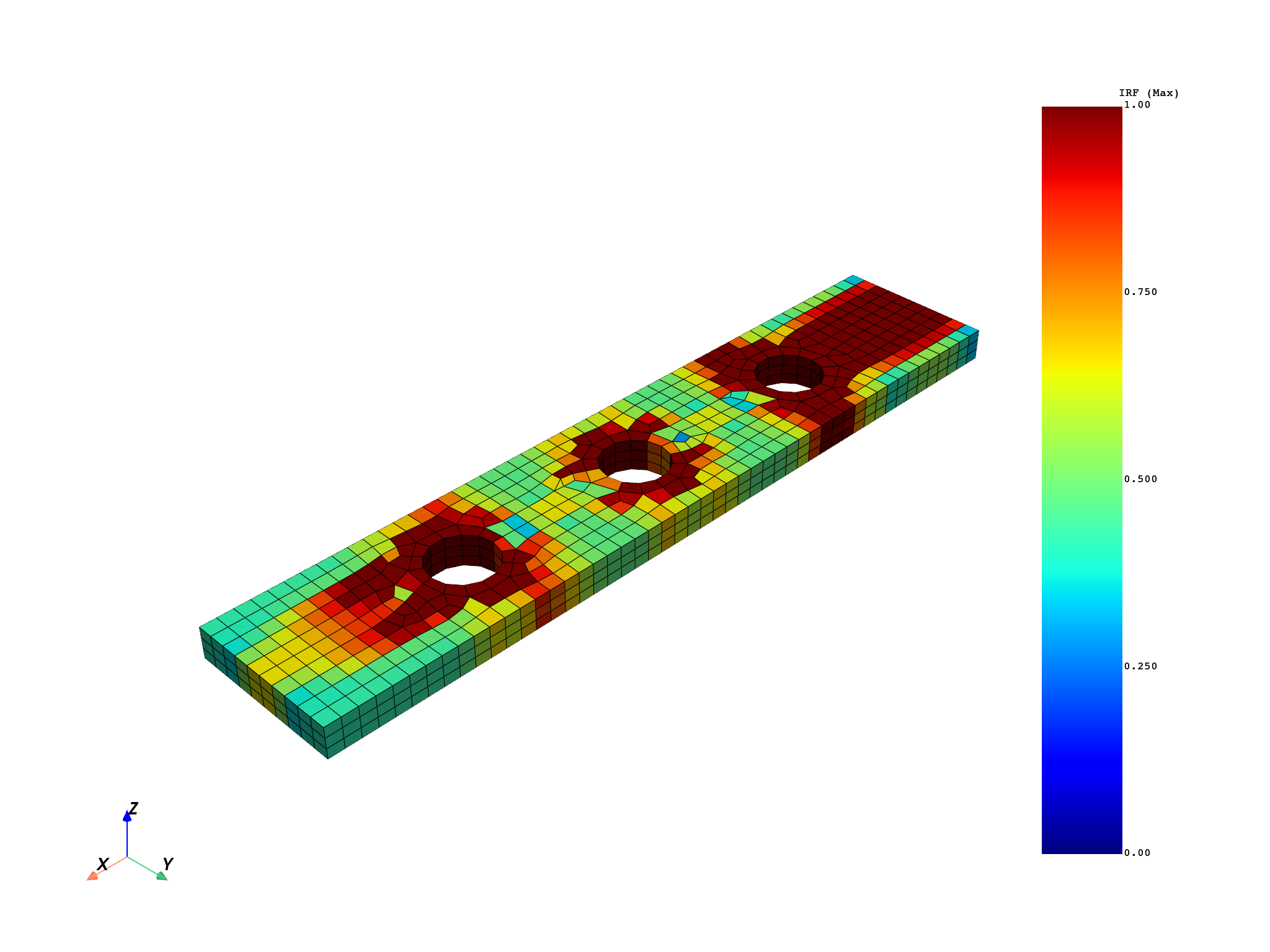
Element scoping#
Postprocess only a subset of elements (1 to 500).
scoping = dpf.Scoping()
scoping.ids = [label for label in range(1, 500)]
evaluate_failure_criterion_op.inputs.element_scoping(scoping)
output = minmax_per_element.outputs.field_max()
plot = model.metadata.meshed_region.plot(output[FailureOutput.FAILURE_VALUE], clim=[0, 1])
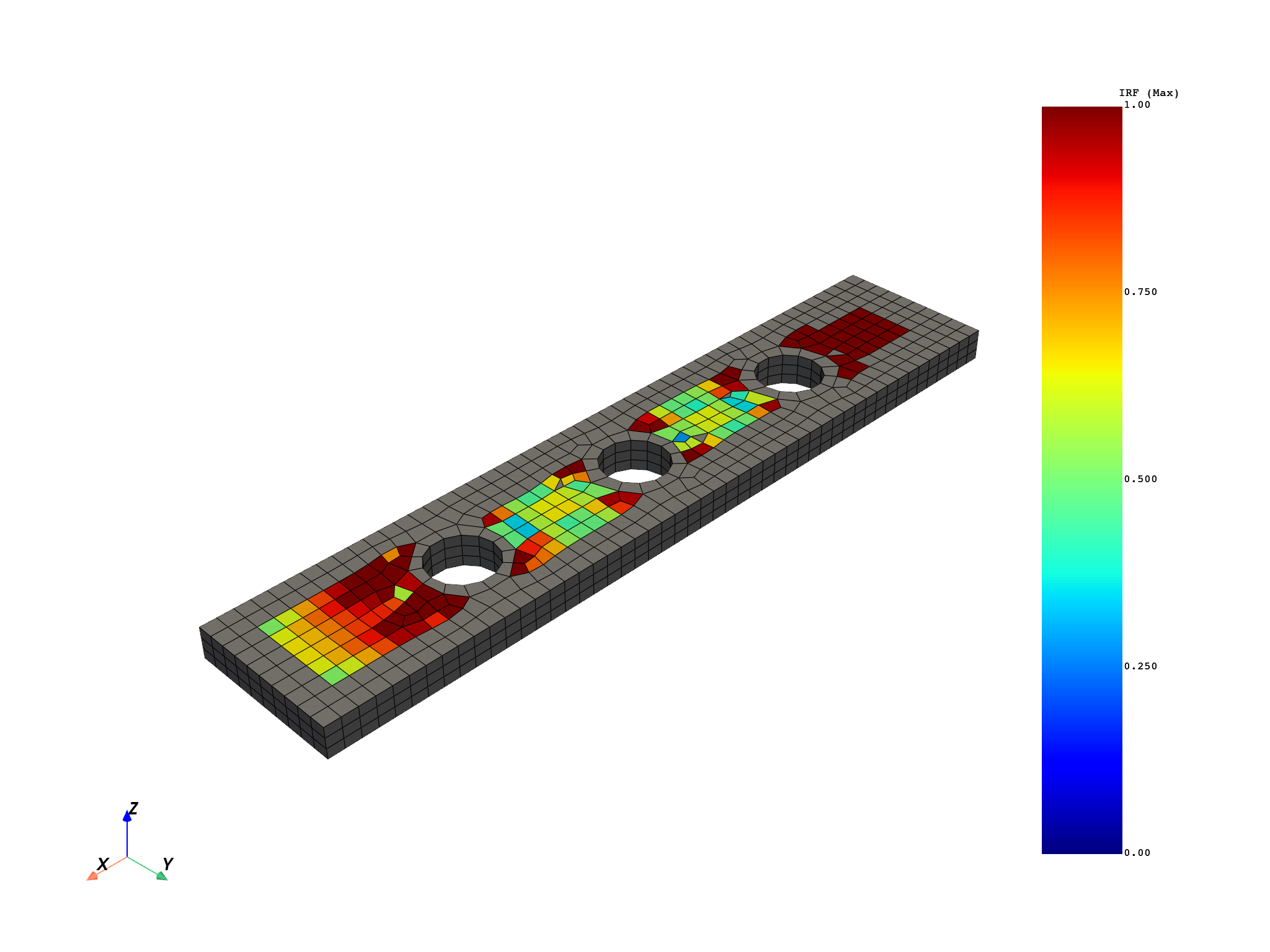
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 6.676 seconds)

